Climate change is a pressing issue that has been a growing concern for scientists, policymakers, and the general public alike. As the Earth’s climate continues to change at an accelerating rate, the concept of irreversible consequences has become a topic of great significance. In this blog post, we will delve into the understanding of irreversible consequences and explore the timeline for when they may occur. We will also examine the current signs of irreversible consequences and the impact of greenhouse gas emissions on our planet. Additionally, we will discuss the factors that are accelerating irreversible consequences and explore mitigation strategies aimed at preventing or delaying them. Finally, we will consider the important role that humans play in addressing climate change and the urgency of taking action to mitigate its potentially devastating effects. Join us as we explore the critical issue of irreversible consequences of climate change and what can be done to address them.
What's in this article :
Understanding the concept of irreversible consequences
Irreversible consequences refer to the lasting and permanent effects of certain actions or events that cannot be undone or reversed. These consequences typically have significant impacts on the environment, ecosystems, and human society. It is crucial to recognize and comprehend the concept of irreversible consequences in the context of environmental degradation and climate change.
Understanding the concept involves acknowledging the irreversible loss of biodiversity, destruction of natural habitats, and depletion of natural resources. These consequences are the result of human activities such as deforestation, industrial pollution, overconsumption, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Moreover, the concept of irreversible consequences emphasizes the urgency of taking proactive measures to mitigate and prevent further irreversible damage to the planet. It highlights the interconnectedness of ecological systems and the need for sustainable practices to preserve the Earth’s delicate balance.
Ultimately, understanding irreversible consequences serves as a catalyst for promoting environmental stewardship, conservation efforts, and the adoption of sustainable technologies and policies to safeguard the planet for future generations.
Predicting the timeline of irreversible consequences
When it comes to irreversible consequences due to climate change, a major concern is the unpredictability of when these consequences will occur. The timeline of irreversible consequences is a pressing issue that scientists are working to understand and predict.
It is clear that the Earth is already experiencing the effects of climate change, but the timeline of irreversible consequences, such as the melting of polar ice caps and the extinction of certain species, is still uncertain. This uncertainty makes it difficult for policymakers and communities to prioritize actions to address climate change.
However, through the use of advanced climate models and data analysis, scientists are making progress in predicting the timeline of irreversible consequences. By studying past climate patterns and the current rate of greenhouse gas emissions, researchers can make educated estimates about when certain irreversible consequences may occur.
While the timeline of irreversible consequences may still be a topic of debate and ongoing research, the importance of understanding and predicting these outcomes is crucial for implementing effective strategies to mitigate climate change and protect the planet for future generations.
Current signs of irreversible consequences
Climate change is one of the most pressing issues of our time, and it is already causing irreversible consequences around the world. The melting of polar ice caps and glaciers is a clear sign of the impact of global warming. As the temperature of the planet continues to rise, ice melts at a faster rate, leading to rising sea levels and the potential displacement of millions of people living in coastal areas. This phenomenon is not only a sign of irreversible consequences, but also a warning sign for the future.
Another visible sign of irreversible consequences is the increase in extreme weather events such as hurricanes, droughts, and wildfires. These events are becoming more frequent and severe, causing immense damage to infrastructure, agriculture, and human life. As the planet warms, these extreme events will continue to escalate, posing a threat to the stability of ecosystems and communities.
Furthermore, the acidification of the oceans is a clear indicator of irreversible consequences. The absorption of excess carbon dioxide by the oceans has led to a decrease in pH levels, affecting marine life and ecosystems. This phenomenon not only disrupts the balance of marine ecosystems but also has far-reaching consequences for global food security and biodiversity.
Lastly, the loss of biodiversity is a critical sign of irreversible consequences. The extinction of plant and animal species due to habitat loss, pollution, and climate change is a direct result of human activities. This loss of biodiversity not only threatens the stability of ecosystems but also impacts the well-being of human populations, as it disrupts the delicate balance of the natural world.
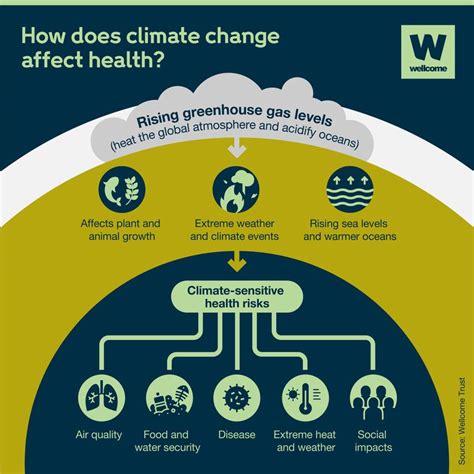
The impact of greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions have become a major concern in the modern world, as their impact on the environment becomes increasingly clear. The release of these gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, contributes to the greenhouse effect, which leads to a rise in global temperatures.
This rise in temperature has a range of effects on the environment, including the melting of polar ice caps, rising sea levels, and extreme weather events. These changes can have a significant impact on ecosystems, leading to the loss of biodiversity and disruptions to natural habitats. Furthermore, the warming of the oceans can lead to the bleaching of coral reefs and the disruption of marine life.
The impact of greenhouse gas emissions is also felt on a societal level, as communities are affected by the consequences of climate change. This can include increased frequency and severity of natural disasters, such as hurricanes, floods, and droughts, leading to displacement and loss of livelihoods for many people.
In addition, the economic impact of these environmental changes can be significant, affecting industries such as agriculture, fishing, and tourism. Furthermore, the health of individuals can be affected by air and water pollution resulting from the release of greenhouse gases, leading to respiratory issues and other health problems.
Factors accelerating irreversible consequences
Factors accelerating irreversible consequences
Climate change is an undeniable reality that is affecting our planet at an alarming rate. There are various factors that contribute to the acceleration of irreversible consequences associated with climate change. One of the key factors is the increase in greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide and methane, which trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere and lead to global warming.
Another factor that accelerates irreversible consequences is deforestation, which not only reduces the number of trees able to absorb carbon dioxide, but also disrupts the balance of ecosystems and contributes to the release of stored carbon. Additionally, the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers due to rising temperatures is a significant factor that accelerates irreversible consequences, as it contributes to global sea level rise and disrupts ocean currents.
Furthermore, the use of fossil fuels for energy production and transportation is a major factor accelerating irreversible consequences. The extraction and burning of fossil fuels release large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, further exacerbating the greenhouse effect and global warming. Additionally, industrial activities, including manufacturing and mining, release other potent greenhouse gases and pollutants into the atmosphere, contributing to the acceleration of irreversible consequences associated with climate change.
In conclusion, there are multiple factors that are accelerating irreversible consequences associated with climate change, including the increase in greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, melting polar ice caps and glaciers, and the use of fossil fuels for energy production and industrial activities. It is imperative that these factors be addressed through mitigation strategies and collective action to prevent further irreversible consequences and protect the future of our planet.
Mitigation strategies to prevent irreversible consequences
Climate change is a pressing issue that has the potential to cause irreversible consequences for our planet. The increasing concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is leading to rising global temperatures, melting ice caps, and extreme weather events. If left unchecked, these changes could have devastating impacts on the environment, human health, and economies around the world.
Fortunately, there are mitigation strategies that can be implemented to help prevent irreversible consequences. One such strategy is the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. This can be achieved through the use of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power, as well as the implementation of energy-efficient technologies and practices.
Another important mitigation strategy is the protection and restoration of ecosystems such as forests, wetlands, and coral reefs. These natural habitats play a critical role in sequestering carbon dioxide and regulating the Earth’s climate. By preserving and restoring these ecosystems, we can help mitigate the impacts of climate change and prevent irreversible consequences.
Additionally, efforts to promote sustainable agricultural practices and reduce deforestation can also contribute to mitigation. By improving land management and reducing the conversion of forests into agricultural land, we can help to reduce carbon emissions and preserve vital ecosystems.
The human role in addressing climate change
Climate change is a pressing global issue that requires the collective effort of every individual. The human role in addressing climate change cannot be overstated, as our actions directly impact the environment and contribute to the problem at hand.
It is important for everyone to recognize the impact of their daily choices on the environment. From the products we consume to the modes of transportation we use, every decision we make has the potential to either exacerbate or mitigate climate change.
One way in which individuals can contribute to addressing climate change is by adopting sustainable practices in their everyday lives. This could include reducing energy consumption, using renewable resources, and supporting eco-friendly businesses and initiatives.
Furthermore, advocating for policy changes and participating in community-based climate action can also have a significant impact. By raising awareness and pushing for environmental regulations and initiatives, individuals can help pave the way for a more sustainable future.